Customer Health and Safety (FY2021 Report)
Materiality Indicators
Management Approach
Why the topic is material
The Daigas Group puts the highest priority on securing safety of gas supply and facilities as an energy business operator which supplies city gas to 5.031 million customers. Therefore, we consider it important that we make efforts to enhance the safety level and formulate a structure to respond possible accidents and disasters.
Boundary
Within the Group
Management systems and performance
Indicator (GRI Standards: 416-1)
Percentage of city gas supplied by Osaka Gas that undergoes health and safety assessment
Commitment
Osaka Gas is committed to ensuring the safety of city gas, our primary product, its secure supply, and the safety of our gas facilities—all by adhering to our “Security Rules” according to the terms of the Gas Business Law.
(International and domestic standards)
- ・Gas Business Law
(In-house policy and standards)
- ・Daigas Group Code of Business Conduct
- ・Security Rules
Responsibilities
The Daigas Group has established a system to ensure the safety of the city gas supply and gas appliances encompassing all facets of the Group’s city gas value chain — processing, supply, sales, and consumption. The Head of Safety and the individuals heading the safety operations of each business unit and Osaka Gas Network Co., Ltd. supervise safety and security matters concerning their respective business.
In addition, the Executive Safety Council, comprising the Head of Safety; the individuals heading the safety operations of each business unit and Osaka Gas Network Co., Ltd.; and the chiefs of the relevant departments, convene safety and security meetings five times annually to plan safety initiatives and assess the achievements made in the relevant term. In line with the annual plan, each business unit and Osaka Gas Network Co., Ltd. systematically promotes initiatives to ensure security and improve safety.
- * In April 2022, Osaka Gas Network Co., Ltd. took over the city gas pipeline business of Osaka Gas Co., Ltd.
■ Security and Safety Promotion Structure
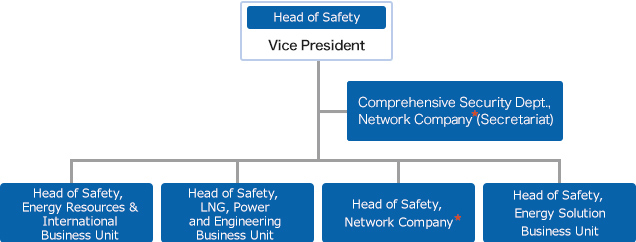
- *Effective April 2022, Osaka Gas Network Co., Ltd. was incorporated as a result of the legal separation of Network Company, the former pipeline business unit of Osaka Gas.
Performance
In FY2021, all procedures were conducted based on guidelines in accordance with laws and regulations as well as in-house rules for processes such as quality control of gas in LNG terminals, safety inspection of gas pipelines and supply facilities, and safety inspection of gas appliances with customer consent.
Specific actions taken regarding materiality
To ensure our customers receive our energy services without worry, we are focused on maintaining the high quality of the city gas we supply while ensuring the stability of our gas supply and the safety of gas-processing and supply facilities.
■ Process of the Gas Business
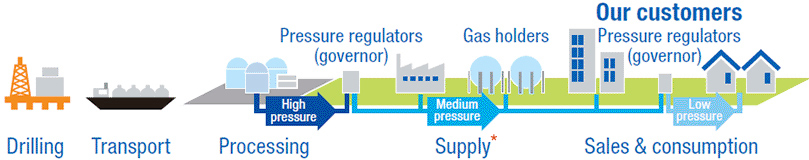
- * In April 2022, Osaka Gas Network Co., Ltd. took over the city gas pipeline business of Osaka Gas Co., Ltd.
Ensuring the quality and safety of city gas
Every day, the city gas plant monitors the quality of the city gas to ensure conformity with the standards set by Osaka Gas according to legal and regulatory requirements. The capacity of the gas holders and gas supply pressure are monitored and well managed in real time.
Inspection of gas pipelines
Gas supply facilities including gas pipes and pressure regulators are inspected to ensure their safety. The frequency and content of such inspections are set under in-house Security Rules.
Securing safety at customers' sites
Facilitate systems to response to reports and prepare resources for dispatching in case of accidents and disasters 24 hours a day, 365 days a year.
In accordance with laws, inspection of gas appliances for gas leaks, gas water heaters for air supply and exhaust function at customers' sites at least once every four years (at least once a year for some customers) were conducted. The visits to the customers were exploited as the opportunity for recommending installation of alarms for gas leaks for residential use and ventilation for commercial use, of which penetration rate were 50.1% and 98.5%, respectively. We are conducting replacement of old gas pipes with new ones that are resistant to earthquakes and corrosion. We are actively proposing the renewal of corrosion-prone old gas pipes by contacting affected customers. In FY2016, we implemented measures to deal with old gas pipes made of gray cast far ahead of the initial schedule of FY2021. We are continuing to take measures against old gas pipes made of gray cast iron (gas pipes requiring maintenance and management) and corrosion-prone gas pipes.
Disaster preparedness
After our experience with the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake in 1995, we have implemented a variety of earthquake countermeasures, also adding new measures devised based on our experience with the 2018 Northern Osaka Prefecture Earthquake. Those efforts include the enhancement of safety measures in city gas manufacturing facilities, the replacement of old gas pipes with polyethylene (PE) pipes (approx. 17,200 km installed) that offer excellent durability and seismic resistance, and the installation of intelligent meters that detect earthquake vibrations and shut off the gas supply (approximately 99.9% of all meters and 100% of residential meters).
As an emergency measure, we are constructing a system for shutting off the gas supply to prevent secondary disasters. Automatic seismic detection/remote shutoff devices are being installed (now in approx. 3,000 and 3,600 locations, respectively) that automatically shut off the low-pressure gas supply in the supply area when a large earthquake is detected.
Since the March 2011 earthquake and tsunami that struck northeastern Japan, we have been redoubling our tsunami countermeasures. Standby generators installed at LNG terminals have been reinforced, the watertightness* of the structures housing equipment at the terminals has been improved, and some of the equipment has been moved to higher locations to avoid a tsunami. To prevent secondary damage and facilitate the early recovery of gas supply, one system being introduced is a damage-reduction block system that controls the gas supply of medium- and low-pressure gas pipes installed in coastal areas. In addition to these physical measures in the event of a tsunami, other steps are being taken, such as holding Company-wide Comprehensive Disaster Response Drills and providing emergency training. We expect these disaster-prevention efforts to establish a robust and resilient value chain in city gas service.
(Figures current as of March 31, 2021.)
-
* Watertightness
Resistance to flooding from a tsunami
■ Security Measures Prepared for a Major Earthquake
| Security Measures Prepared for a Major Earthquake | Status of implementation (as of the end of March 2021)* | |
|---|---|---|
| (1) Reinforcement of an information collection function | Installation of seismograph | Installed in all areas (3,300 locations) |
| Introduction of an earthquake damage prediction system | Introduced to the Central Control Room (Head Office / Sub-center) and all five districts | |
| (2) Building of a supply shutoff system | Subdivision of supply blocks | Divided into medium-sized blocks (86) and small blocks (660) |
| Introduction of supply shutoff devices | Remote shutoff devices: approx. 3,600 locations Automatic seismic shutdown systems: approx. 3,000 locations |
|
| (3) Others | Efforts to diffuse polyethylene (PE) pipes | Polyethylene (PE) pipes to be used for all new low-pressure pipelines, in principle Total extended length of PE pipes: about 17,200 km |
| Diffusion of an intelligent meter that detects earthquake vibrations | Completed installation for home use, with an overall penetration rate of 99.9% including business customers. | |
| Backup of critical online systems | Establishment of a backup center | |
- * Subdivision of supply block as of April 1, 2021
Energy Transition 2030 Sustainability Report(9.5MB) Integrated Report(12.5MB)
- Management Plan
- Management Plan Documents Long-Term Management Vision 2030 Medium-Term Management Plan 2023
- Daigas Group's Values
- Daigas Group's Values Daigas Group Corporate Principles Daigas Group Charter of Business Conduct Daigas Group Code of Business Conduct Our Declaration Daigas Group Policies
- Sustainability Management
- Promotion System Materiality Stakeholder Engagement History of Co-creation of Value Value Creation Process
- Environment
- Environment Environmental Management Daigas Group Environmental Policy Estimation Method of Environmental Accounting Environmental Management Efficiency Environmental Impact throughout the Daigas Group Value Chain Environmental Targets Actions for Climate Change Assessment of CO₂ Emissions Reduction Effects Disclosure based on the TCFD Recommendations, Recognition of and Actions on Risks and Opportunities Contributing to the Resource-Recycling Society Data Trends Regarding Resource Recycling Information Disclosure on the Research Results of Soil and Groundwater Conservation Biodiversity Daigas Group Biodiversity Policy Development of Environmental Technology
- Social
- Social Innovation Management Human Resources Management Human Resources Development Diversity and Inclusion Daigas Group Diversity Promotion Policy Work-life Balance Occupational Health and Safety Health and Safety Action Plan Communication Between Employees and Company Human Rights Daigas Group Human Rights Policy Supply Chain Management Daigas Group Procurement Policy Social Impact of Business Activities in Our Energy Value Chain Customer Health and Safety Improvement of Customer Satisfaction Community
- Governance
- Governance Corporate Governance Message from the Outside Directors Compliance Consultations and Reports from Partner Companies Information Security Protect Personal Information
- Reporting Guidelines
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Index SASB Table Reference for the Environmental Reporting Guidelines of the Ministry of the Environment TCFD Recommendations Table
