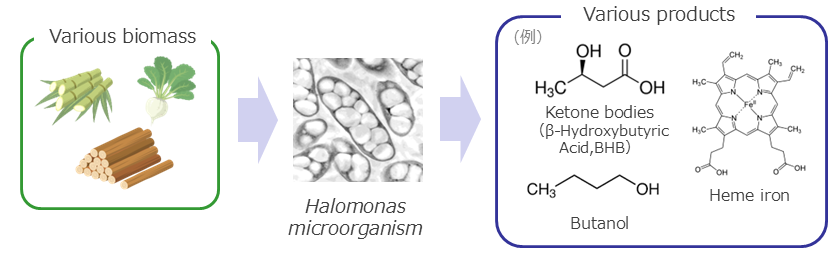
Materials development
Low-cost, Highly Dispersive Multilayer Graphene
- Overview
- Production Process and Characteristics of Multilayer Graphene
- Fabricated Multilayer Graphene
- Physical property 1: Thermal conductivity/heat dissipation
- Physical property 2: Lubricity (friction/wear reduction)
- Physical property 3: Strength (reinforcement of plastics/rubber)
- Physical property 4: Electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics
- Forms of Supply and Use
- Future Development
Overview
Graphene, a sheet-shaped nanocarbon, is said to have various properties, such as thermal conductivity, lubricity, strength, electromagnetic wave absorption, and electrical conductivity. Since it has often been produced in small volumes, taking a large amount of time, a low-cost and simple manufacturing method was desired.
Osaka Gas has had success in easily producing multilayer graphene by exfoliating graphite in a single step in water without chemical modification.

Production Process and Characteristics of Multilayer Graphene
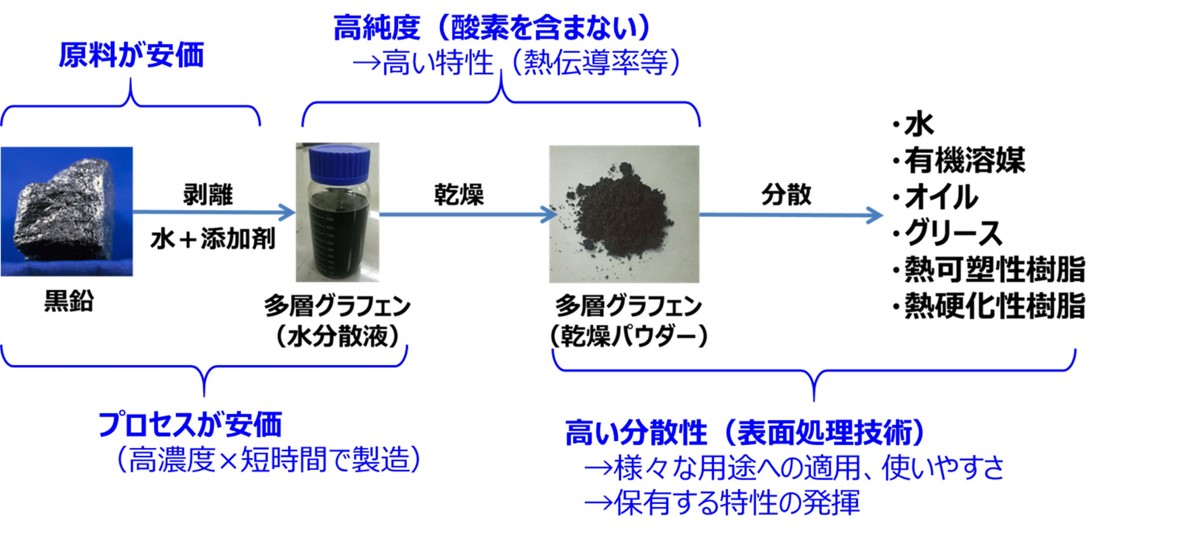
Fig. 1. Production Process and Characteristics of Multilayer Graphene
The graphite is exfoliated in water to create graphene in a single step, which is simple and does not damage the graphene structure. In addition, it can be supplied as (1) an aqueous dispersion that is easily dispersed in water-based paints or (2) a powder that is easily dispersed in resin, rubber, oil, solvents, and water.
Fabricated Multilayer Graphene
The produced multilayer graphene is a very thin material with a thickness of 1 to 10 nm.
Therefore, by adding a large number of sheets with a small weight, it is possible to impart the beneficial physical properties of carbon, such as thermal conductivity, lubricity, and the capacity to improve the strength of rubber and plastics.
In particular, the following physical properties are notable.
1)Thermal conductivity/heat dissipation: High thermal conductivity and emissivity for quick heat transfer and heat dissipation.
2)Lubricity: Reduces friction and wear with a small added amount.
3)Strength: Improves the strength of a wide variety of materials, from thermoplastics and rubbers to inorganics.
4)Electromagnetic wave absorption: Multilayer graphene is also capable of absorbing electromagnetic waves without reflecting them.
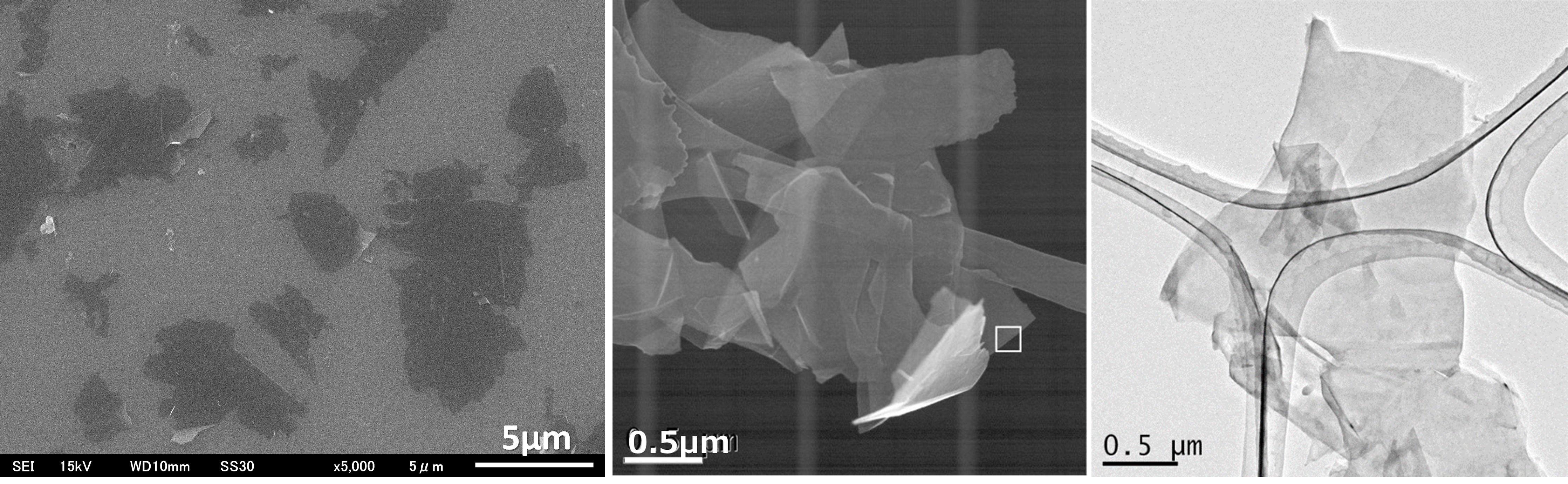 Fig. 2. Electron micrograph of multilayer graphene
Fig. 2. Electron micrograph of multilayer graphene
Physical property 1: Thermal conductivity/heat dissipation






Physical property 2: Lubricity (friction/wear reduction)
A small added amount is effective in reducing friction and wear.
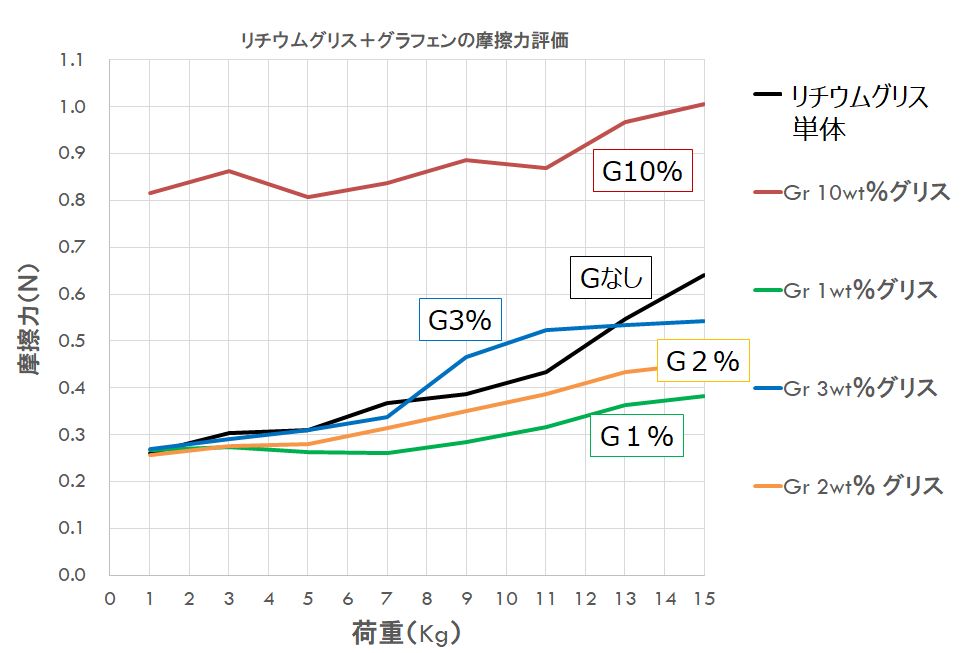
Fig. 8. Friction force due to multilayer graphene-added grease
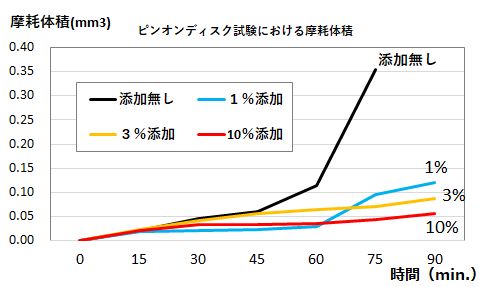
Fig. 9. Amount of wear due to multilayer graphene-added grease
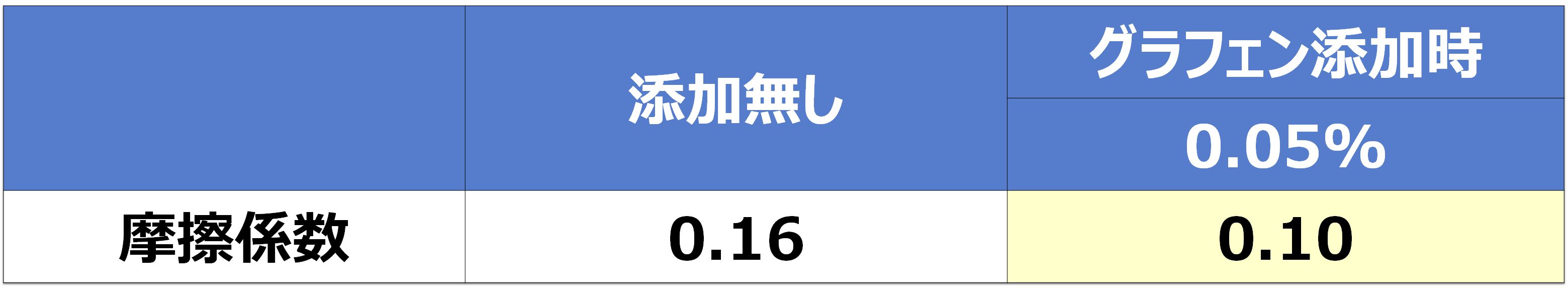
Fig. 10. Friction coefficient due to multilayer graphene-added oil (SRV: vibratory friction and wear test)
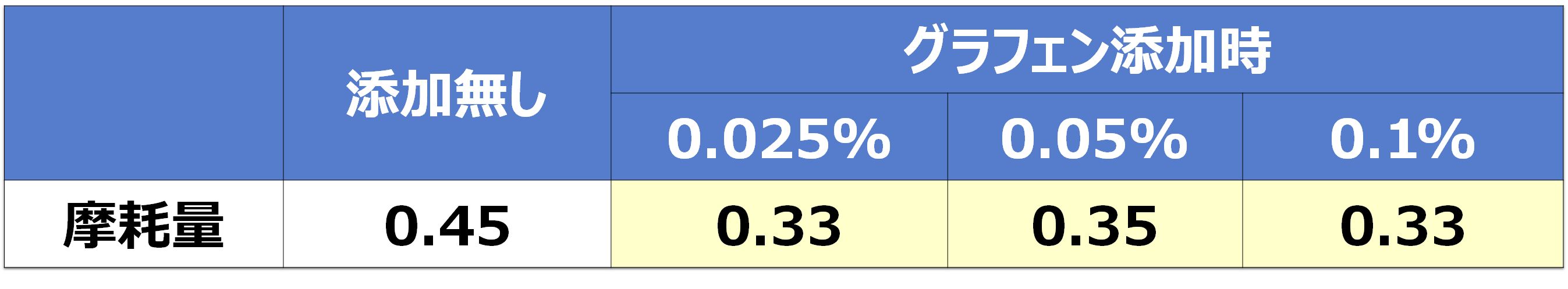
Fig. 11. Amount of wear due to multilayer graphene-added oil (Shell four-ball test: wear)
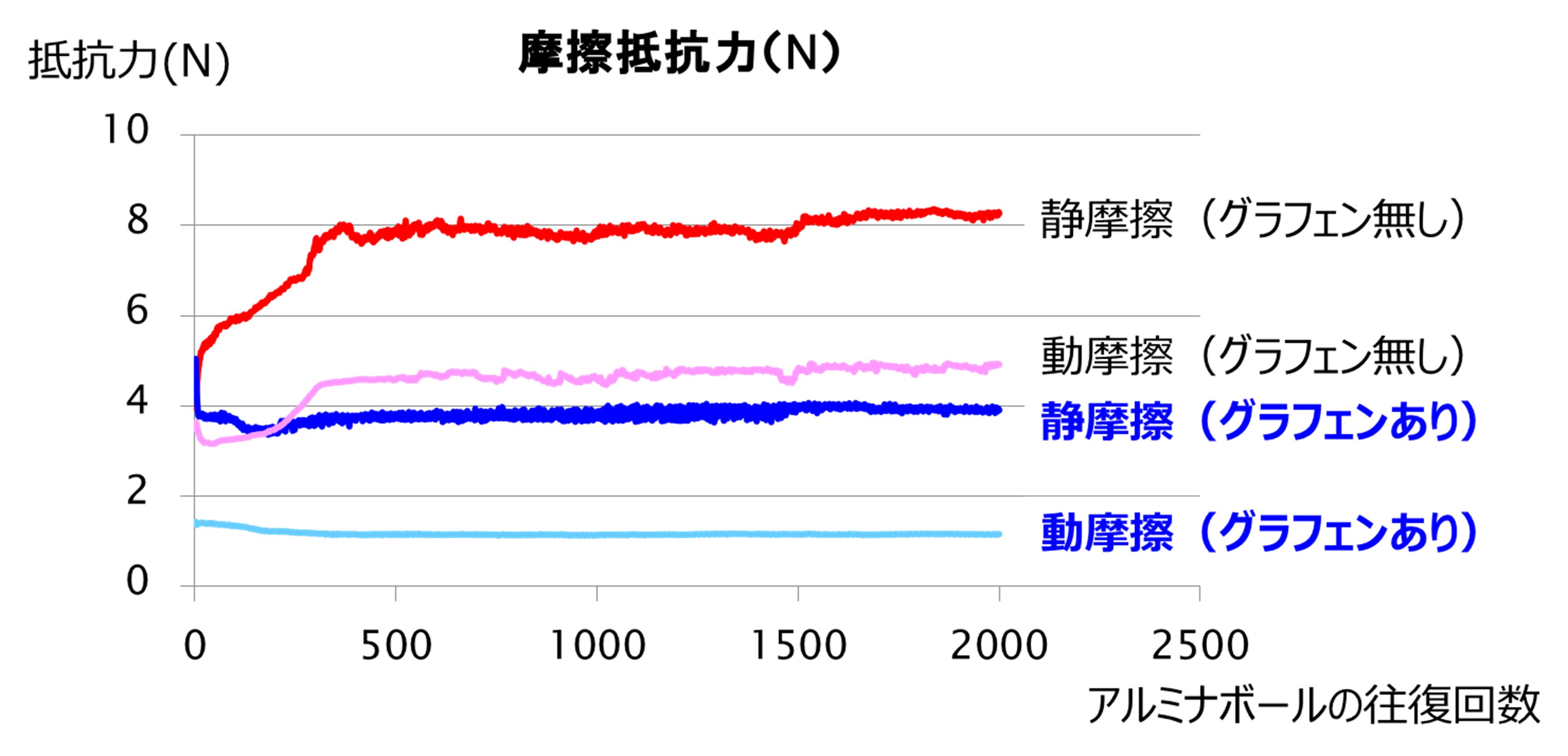
Fig. 12. Friction resistance test of elastomer
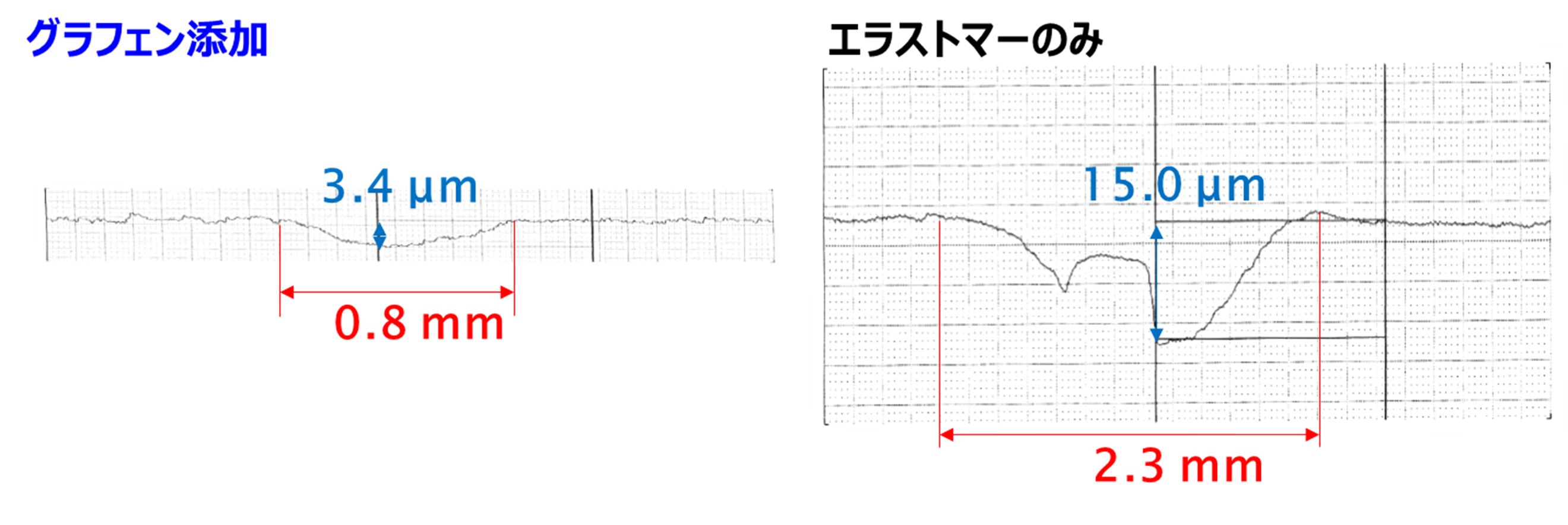
Fig. 13. Comparison of amounts of wear of elastomer
Physical property 3: Strength (reinforcement of plastics/rubber)
・ A small added amount is effective in improving strength and modulus of elasticity.
・ Multilayer graphene has relatively little effect on elongation, impact strength, and tear strength.
・ Improves hardness and wear resistance.
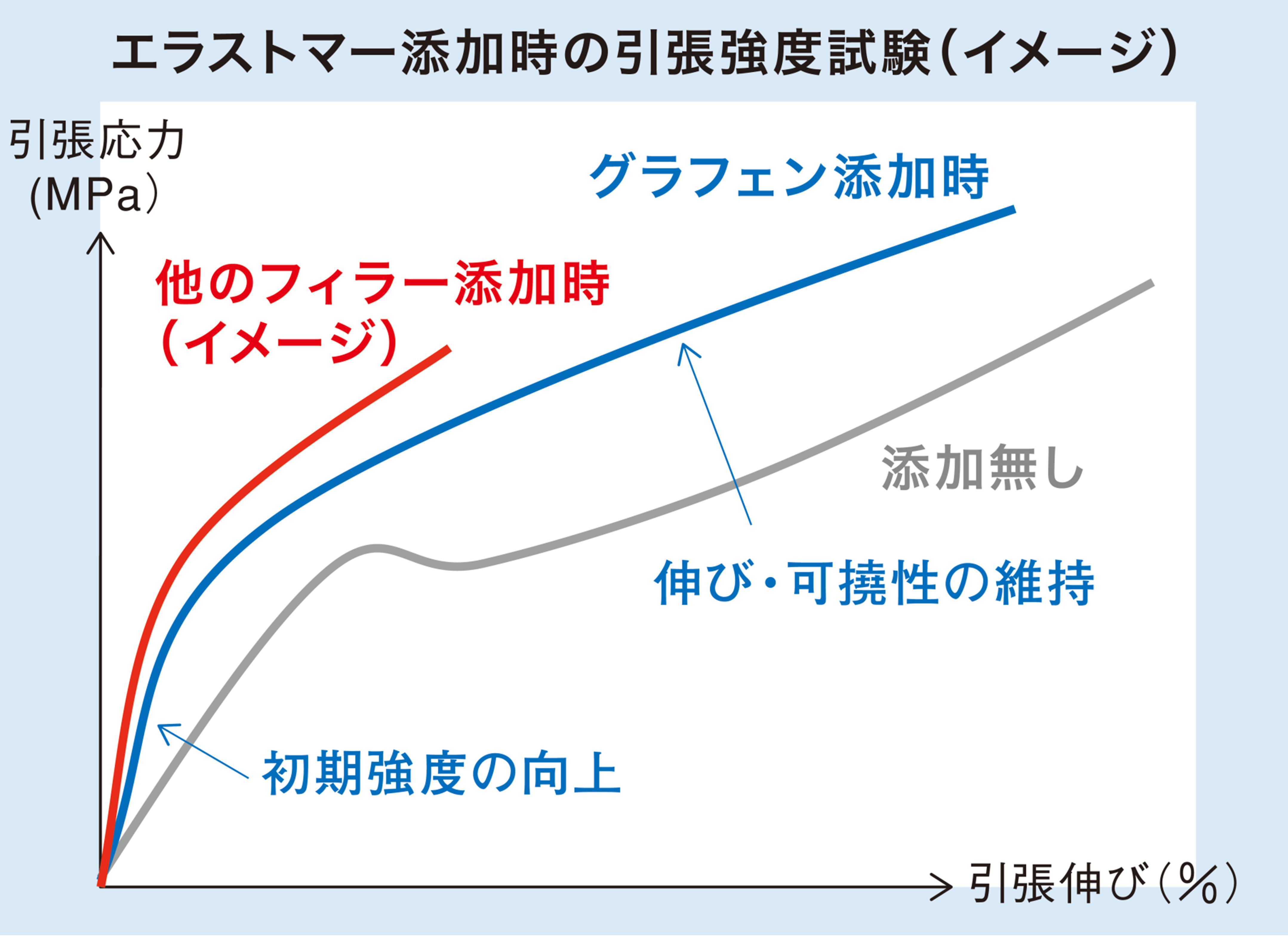
Fig. 14. Tensile strength test of multilayer graphene-added elastomer (rendered image)
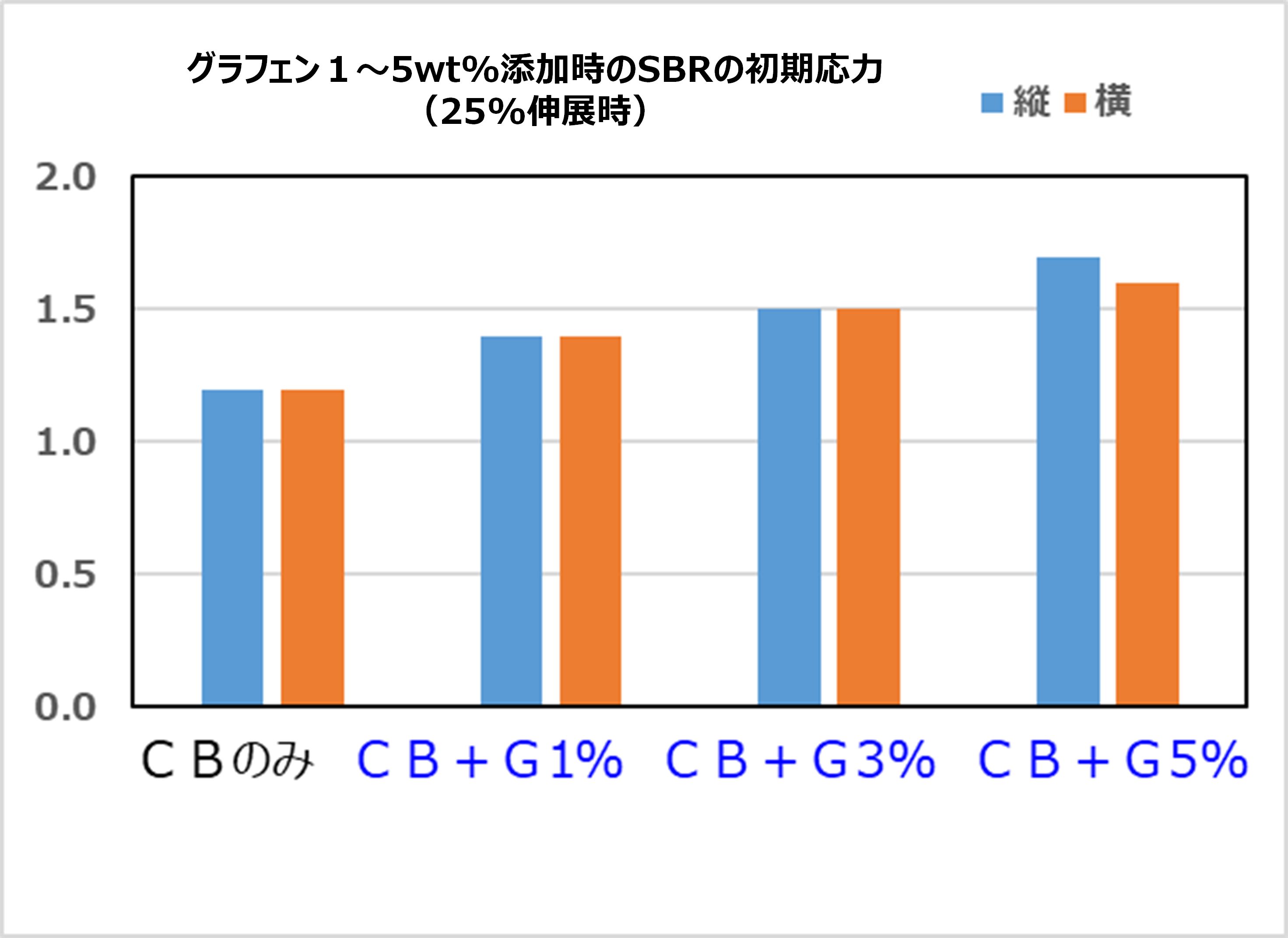
Fig. 15. Initial tensile stress of SBR with a small added amount of multilayer graphene
Physical property 4: Electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics

Fig. 16. Electromagnetic wave absorption characteristics
Forms of Supply and Use
In addition to being dispersed in thermoplastics and thermosetting resin, multilayer graphene can also be added to paints, adsorbed to fibers, and added to oils and greases.
In particular for water-based paint, an aqueous dispersion can be used, which can reduce the effort required for dispersion.
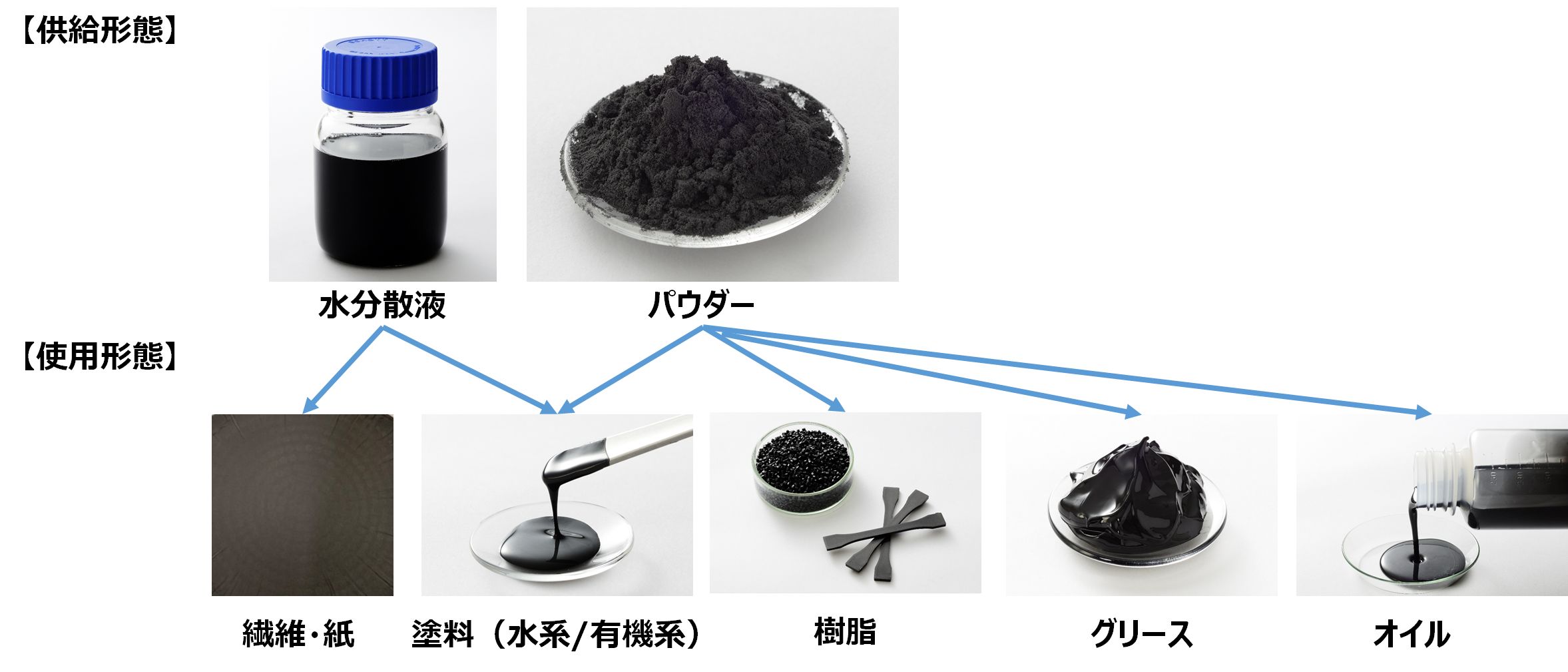

Fig. 17. Forms of supply and use

Fig. 18. Example of addition to existing paint
Future Development
We will develop multilayer graphene suitable for specific uses, such as in composite materials and energy field, etc., and, we will promote mass production to help achieve energy saving and CO2 emissions reduction, safety, and durability improvement.
Related contents
TAG SEARCH
- Evolving residential gas appliances
- Evolving residential gas appliances Water heaters, space heaters, dryers Cooking appliances Smart Equipment Fuel Cell systems
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances Cogeneration (CHP) units Air conditioning systems, kitchen appliances Bio, water treatment Industrial furnaces, burners Energy management, IoT
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification Utilization of cold energy Plant materials Power generation technology
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives Materials development Measurement Simulation, data analysis Food science Material evaluation
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society Methanation Hydrogen, ammonia Biogas Energy management Renewable Energy
- Technologies of Group companies
- KRI, Inc. Osaka Gas Chemicals Group OGIS-RI Group