Fuel Cell systems
IoT-Enabled Next-Generation Quality Management for ENE-FARM
- Overview
- Next-Generation Quality Management Initiatives
- Market Response Comparison: With and Without Always-On IoT Connection
- Predictive Failure Logic: Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Approaches
- Case Study: Failure Prediction Using Unsupervised Learning (Flow Meter Anomaly)
- Strategic Outcomes and Future Initiatives
Overview
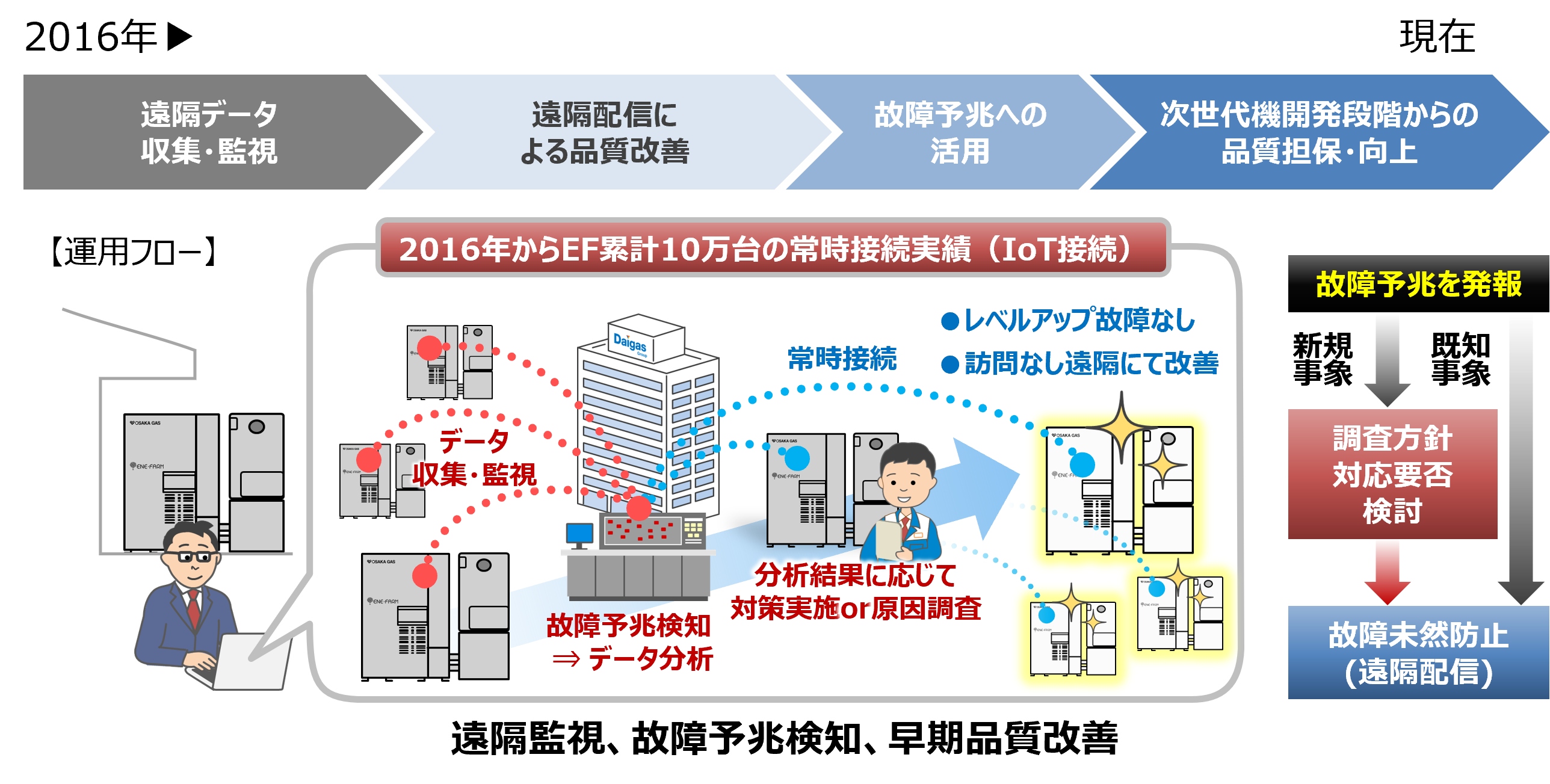
Since fiscal 2016, we have leveraged IoT in ENE-FARM type S to remotely collect operational data from units in the field and apply advanced data analytics to product quality management, thereby reducing equipment failures at customer sites.
Next-Generation Quality Management Initiatives
Our next-generation quality management initiatives are guided by four key objectives:
initiating quality improvements even before the first failure occurs;
enhancing the quality of in-market units without requiring onsite visits;
preventing failures through AI-based predictive failure logic; and
identifying and eliminating potential failure modes from the early stages of product development.
Since 2016, the real-time collection and monitoring of operational data from always-connected ENE-FARM units have enabled early detection of initial failures, including those caused by manufacturing variability. Based on these insights, we have implemented countermeasures and enhanced device control remotely, achieving tangible quality improvements without the need for onsite visits.
By leveraging big data obtained through continual connectivity and applying AI technologies, we have developed predictive failure logic capable of detecting subtle deviations from normal operating conditions—patterns that are difficult to identify through human observation alone. This enables early initiation of root cause analysis and assessment of potential widespread failure risks before issues become apparent in the field.
Market Response Comparison: With and Without Always-On IoT Connection
When always-on IoT connection is available, we can simultaneously identify rising failure trends and initiate root-cause investigations and countermeasure preparation. Because operational data from all units in the field can be analyzed collectively, the lead time required to develop and release countermeasures is significantly reduced. In addition, even when onsite visits are ultimately required, temporary countermeasures can be deployed remotely in advance. This allows us to suppress failure rates at an early stage before field inspections begin.
In contrast, without always-on connection, even if the initial failure recognition and investigation start at the same time, it takes considerably longer to grasp overall failure trends across the market. As a result, countermeasure preparation is delayed, and onsite investigations begin only after failures have already become widespread.
In this way, always-on connection enables rapid confirmation of failure trends through big data, accelerating root-cause identification and the release of effective countermeasures.
Predictive Failure Logic: Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Approaches
For legacy models with specific failure modes that have occurred repeatedly in the past, our Predictive Failure Logic utilizes both Supervised and Unsupervised Learning approaches. Supervised Learning is applied to identify potential risks based on strong correlations with known failure patterns. At the same time, Unsupervised Learning monitors deviations and variances from healthy operational data, enabling the detection of emerging or unforeseen anomalies.
Through always-on connection, operational data are continually monitored. For failure prediction based on Supervised Learning, when a failure precursor is identified, immediate actions are taken, such as onsite maintenance or remote optimization. For failure prediction based on Unsupervised Learning, when a potential anomaly is detected, the data are analyzed and root-cause investigations are conducted to assess whether an actual risk exists. Based on this assessment, appropriate countermeasures are determined to ensure sustained product quality.
Case Study: Failure Prediction Using Unsupervised Learning (Flow Meter Anomaly)
Using normal operational data continually collected from our always-connected fleet in the field, we developed a health diagnostic model based on Unsupervised Learning. Through this model, we detected subtle deviations in flow meter measurements as anomalous behavior before any error alerts were triggered. Based on this early detection, the affected components were retrieved and investigated. As a result of the inspection and analysis, foreign object accumulation inside the flow meter was identified as the root cause.
Following this finding, countermeasures were remotely deployed to the fleet before similar errors became widespread in the market. By reducing the likelihood of foreign object accumulation, we successfully prevented a large-scale recurrence of failures and mitigated potential quality issues in advance.
Strategic Outcomes and Future Initiatives
Since the introduction of always-on connection in our 2016 models, we have continually conducted quality management activities based on predictive failure detection, including failure suppression through remote updates. As a result, our current ENE-FARM models have achieved a failure rate comparable to that of conventional residential water heaters.
While these activities are currently focused on ENE-FARM systems, we are also evaluating predictive failure applications for conventional water heaters by leveraging the operational data already available from those products.
Looking ahead, we will further advance proactive maintenance practices to minimize customer inconvenience while also smoothing and balancing maintenance workloads, thereby improving operational efficiency and service quality.
Related contents
TAG SEARCH
- Evolving residential gas appliances
- Evolving residential gas appliances Water heaters, space heaters, dryers Cooking appliances Smart Equipment Fuel Cell systems
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances
- Evolving commercial and industrial gas appliances Cogeneration (CHP) units Air conditioning systems, kitchen appliances Bio, water treatment Industrial furnaces, burners Energy management, IoT
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification
- Enhancing the safety and economic efficiency of LNG regasification Utilization of cold energy Plant materials Power generation technology
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives
- Developing next-generation businesses through enterprising initiatives Materials development Measurement Simulation, data analysis Food science Material evaluation
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society
- Contributing to conserving the environment and achieving a carbon neutral society Methanation Hydrogen, ammonia Biogas Energy management Renewable Energy
- Technologies of Group companies
- KRI, Inc. Osaka Gas Chemicals Group OGIS-RI Group